The satellite-retrieved
Vitamin D weighted UV doses over the period July 1983 to June 2007 were
compared to ground-based measurements at four European
sites. In accordance with the validation of erythemal daily doses we applied a
threshold filter of 200 J/m2 to the daily doses, so that only doses
exceeding that value were included in the validation analysis.
The results detailed in the table beneath show that the
overestimation of the Vit D doses at four stations that could
provide data is roughly of the same order that is seen in the Erythemally
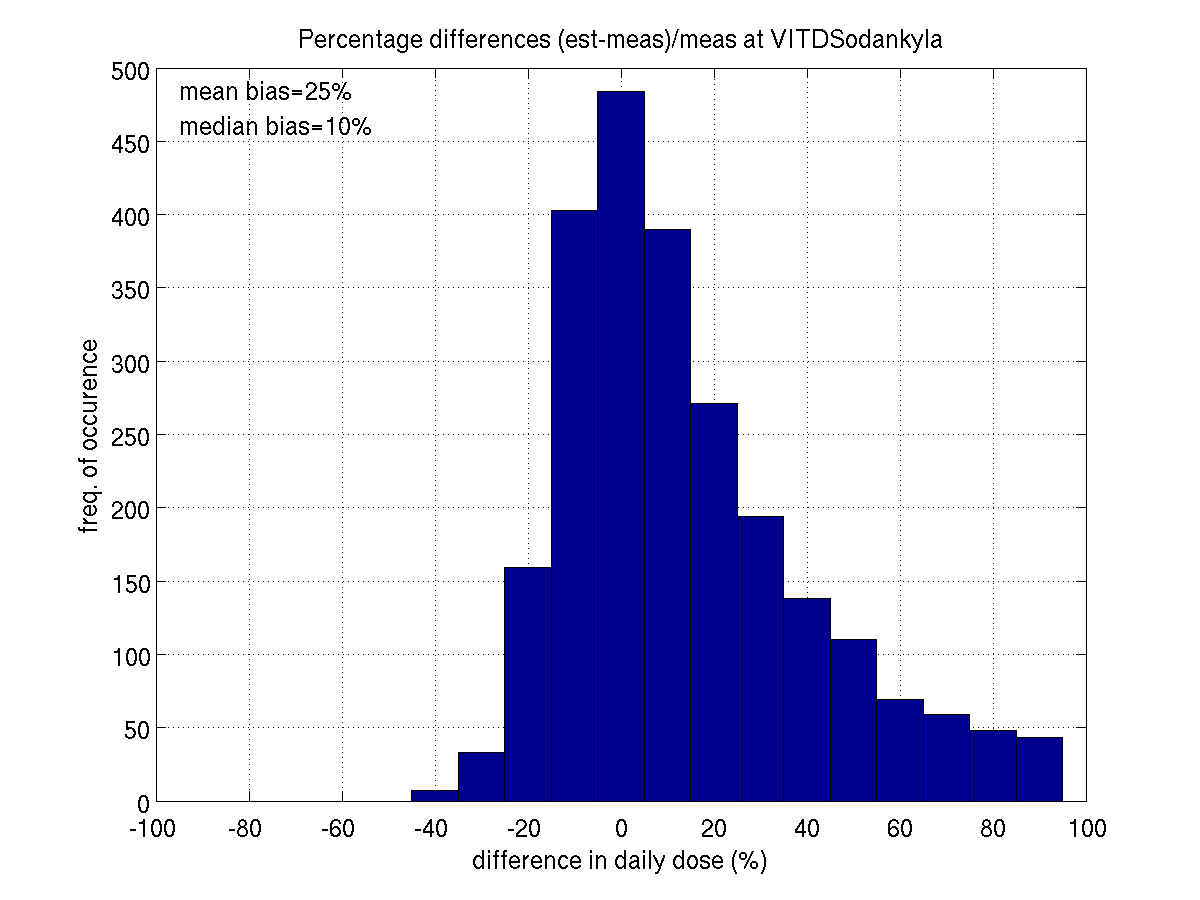
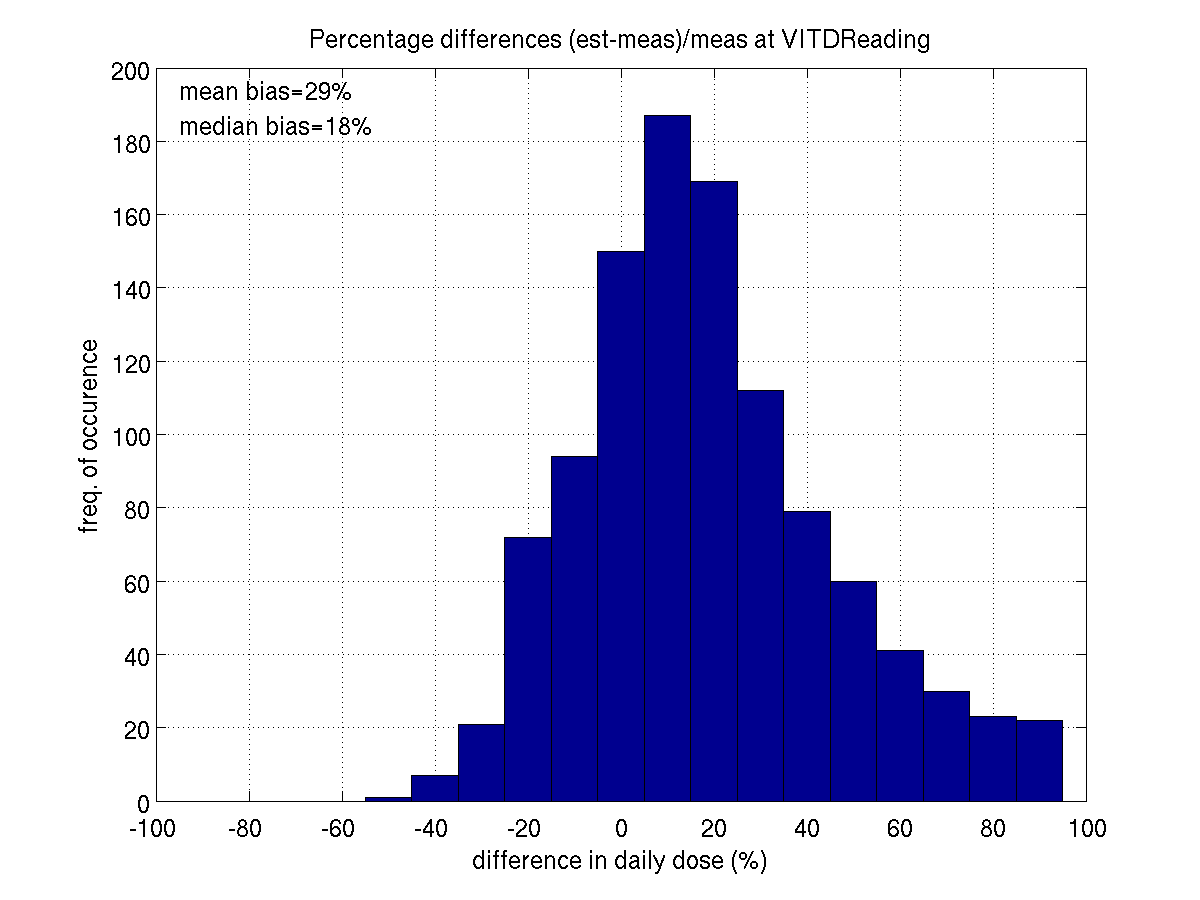
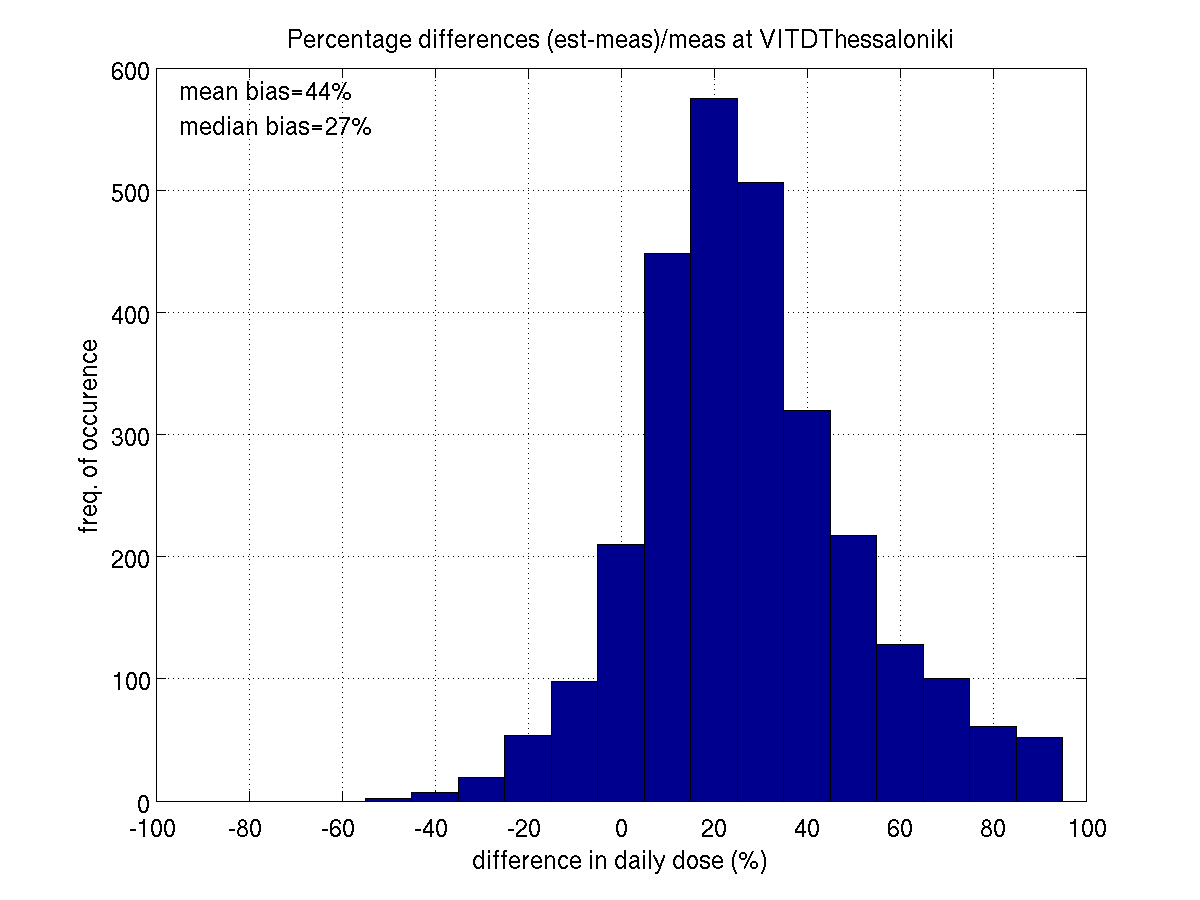
weighted data: mean bias is about 25-30% and median bias 10-20%. However,
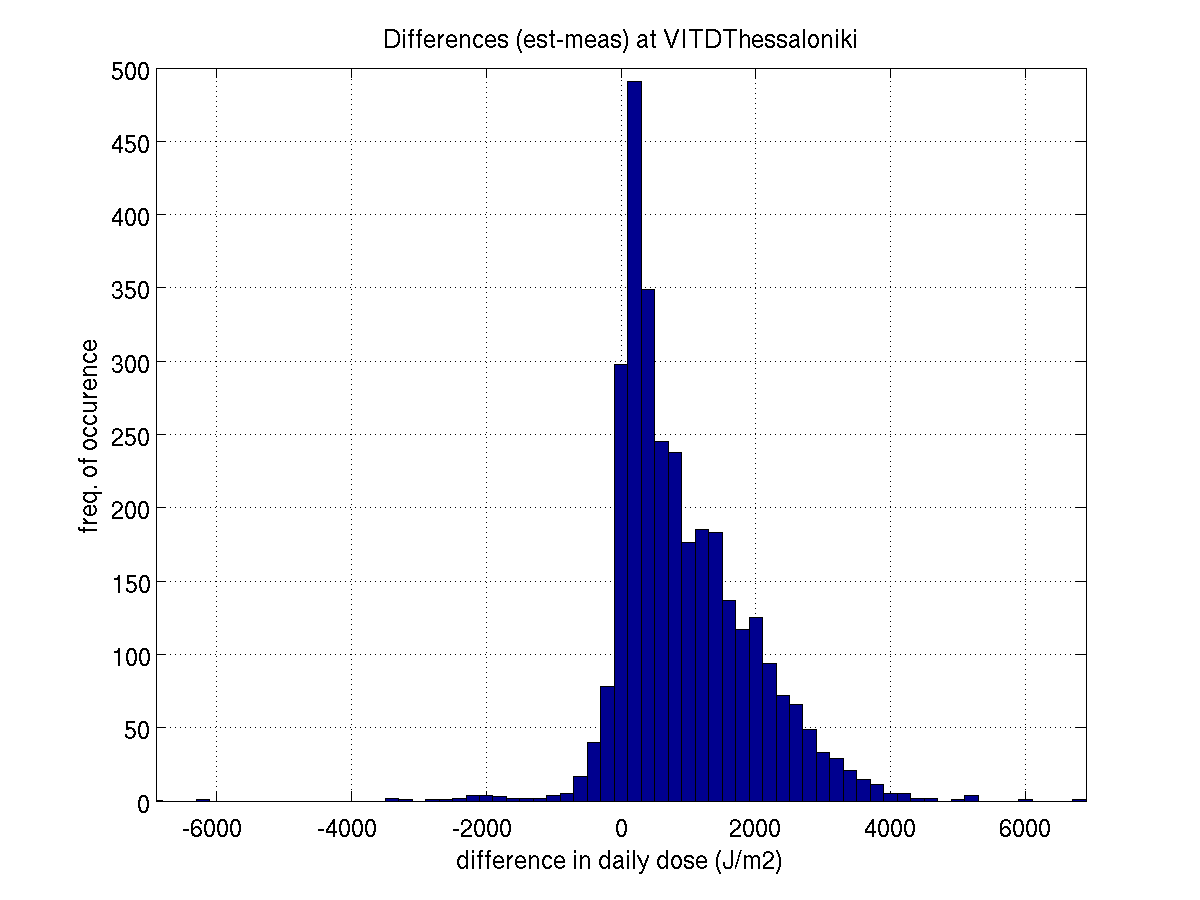
in Thessaloniki the bias in Vitamin D doses is larger than bias for Erythemal
doses.
Table 1. Results of the statistical error analysis. Numbers in table cells are also links
to correspoding figures (link opens in new window)
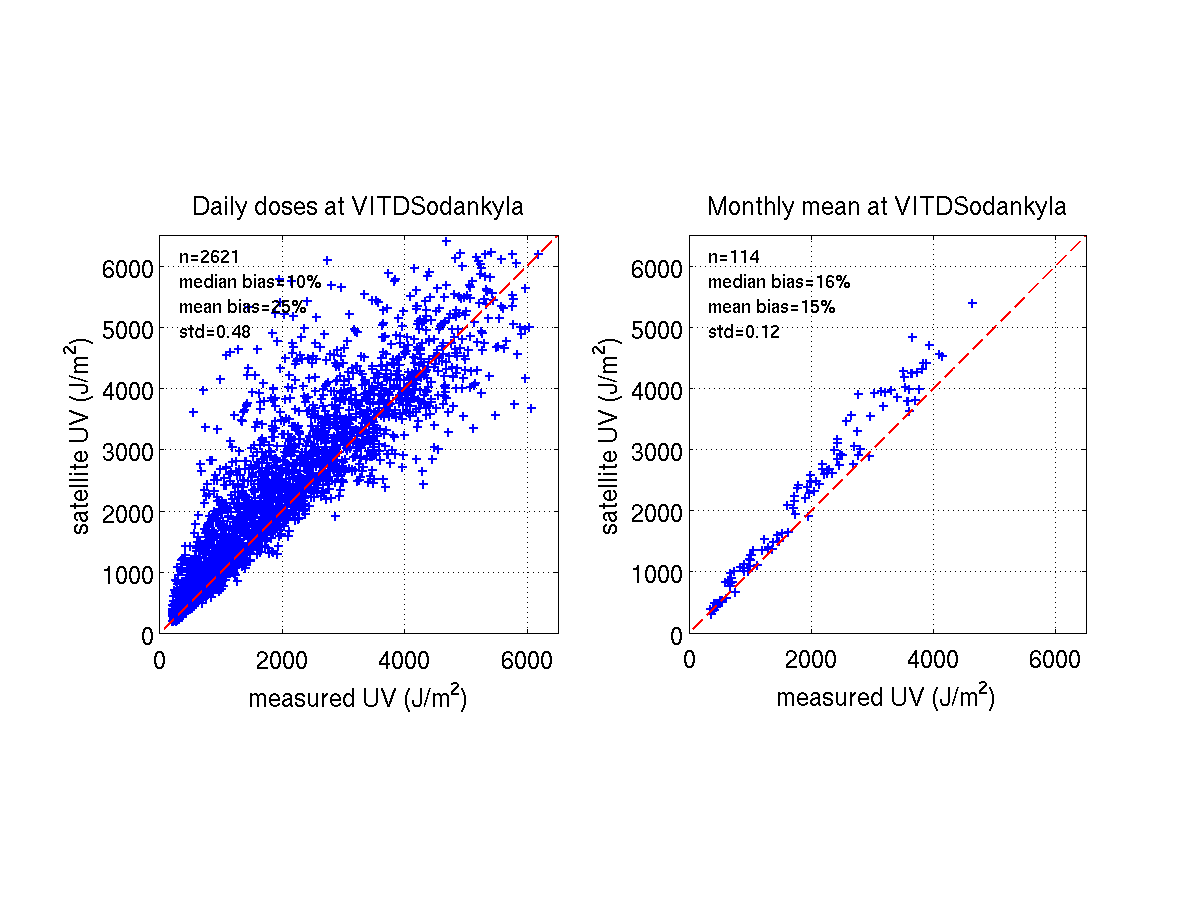
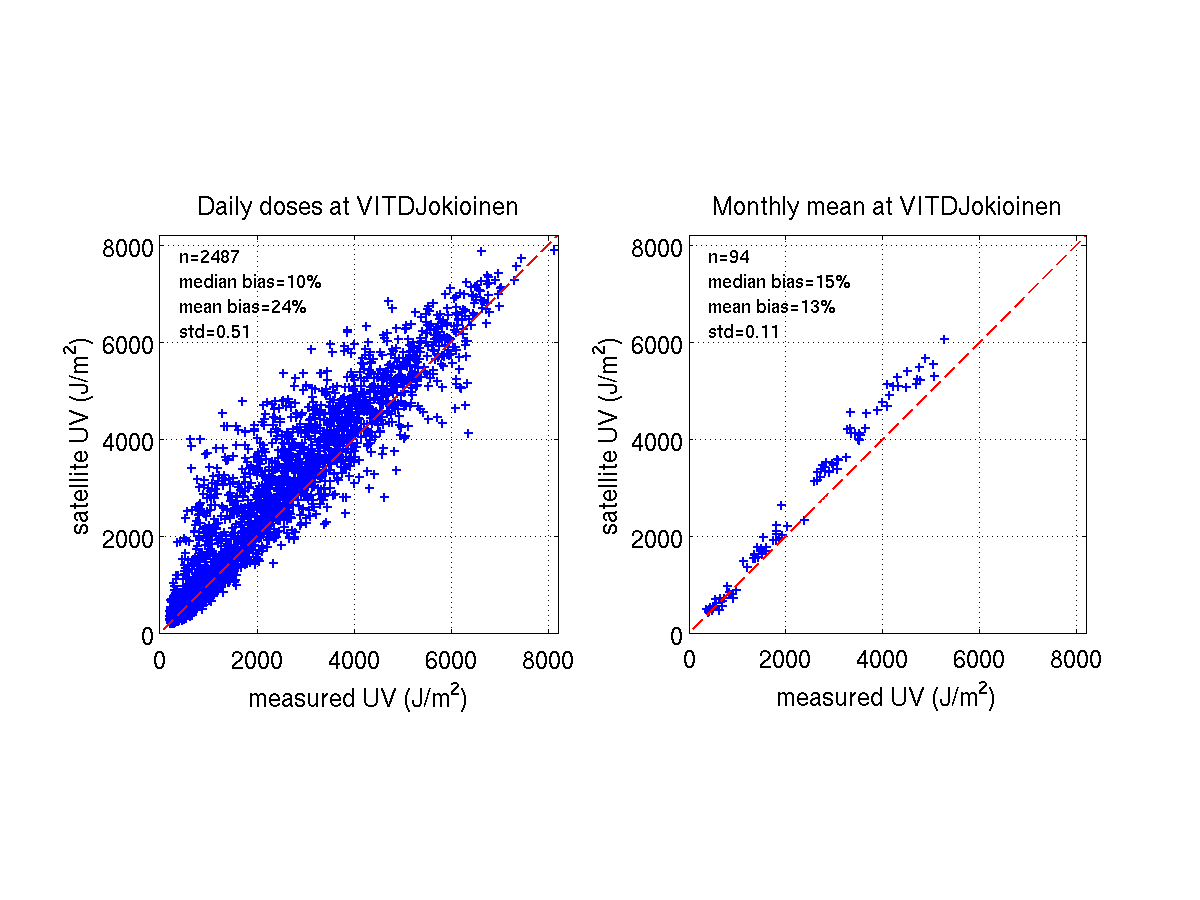
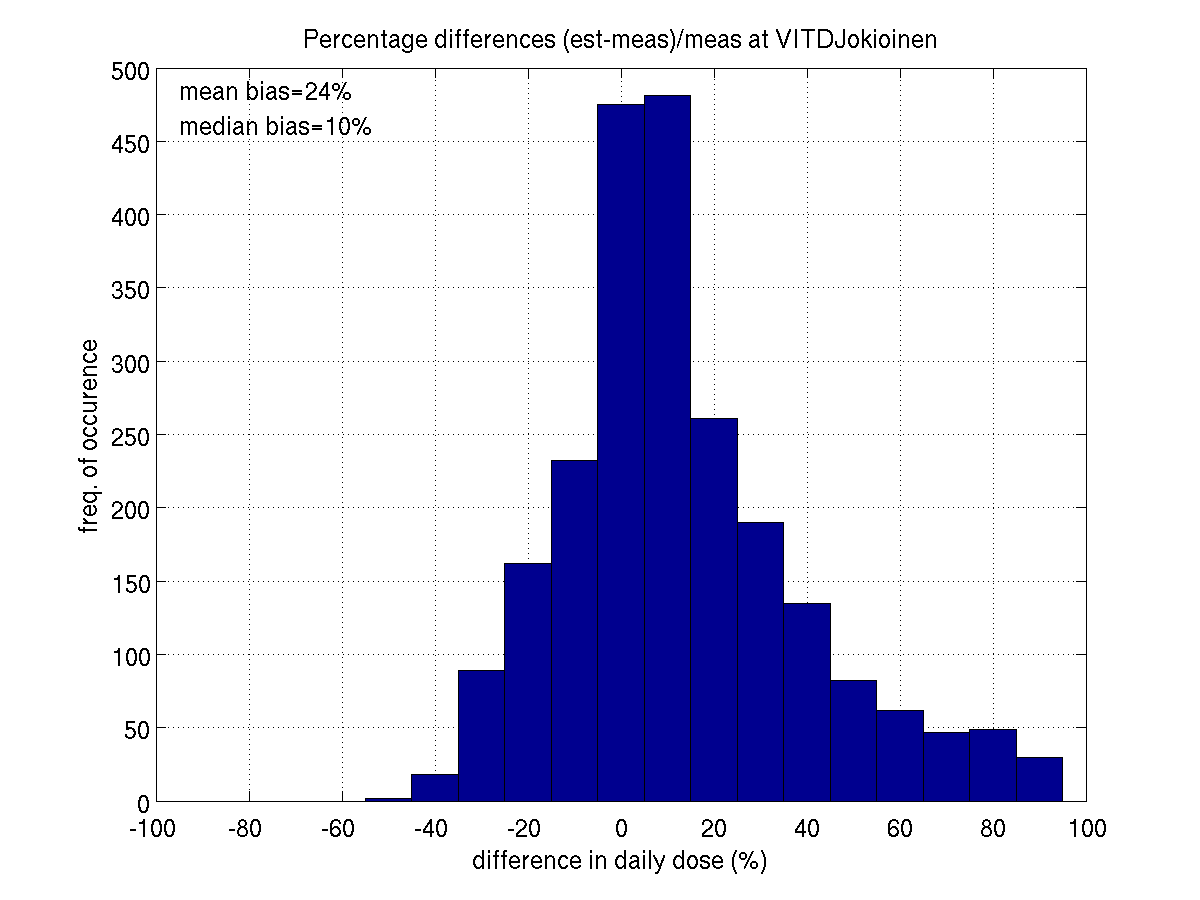
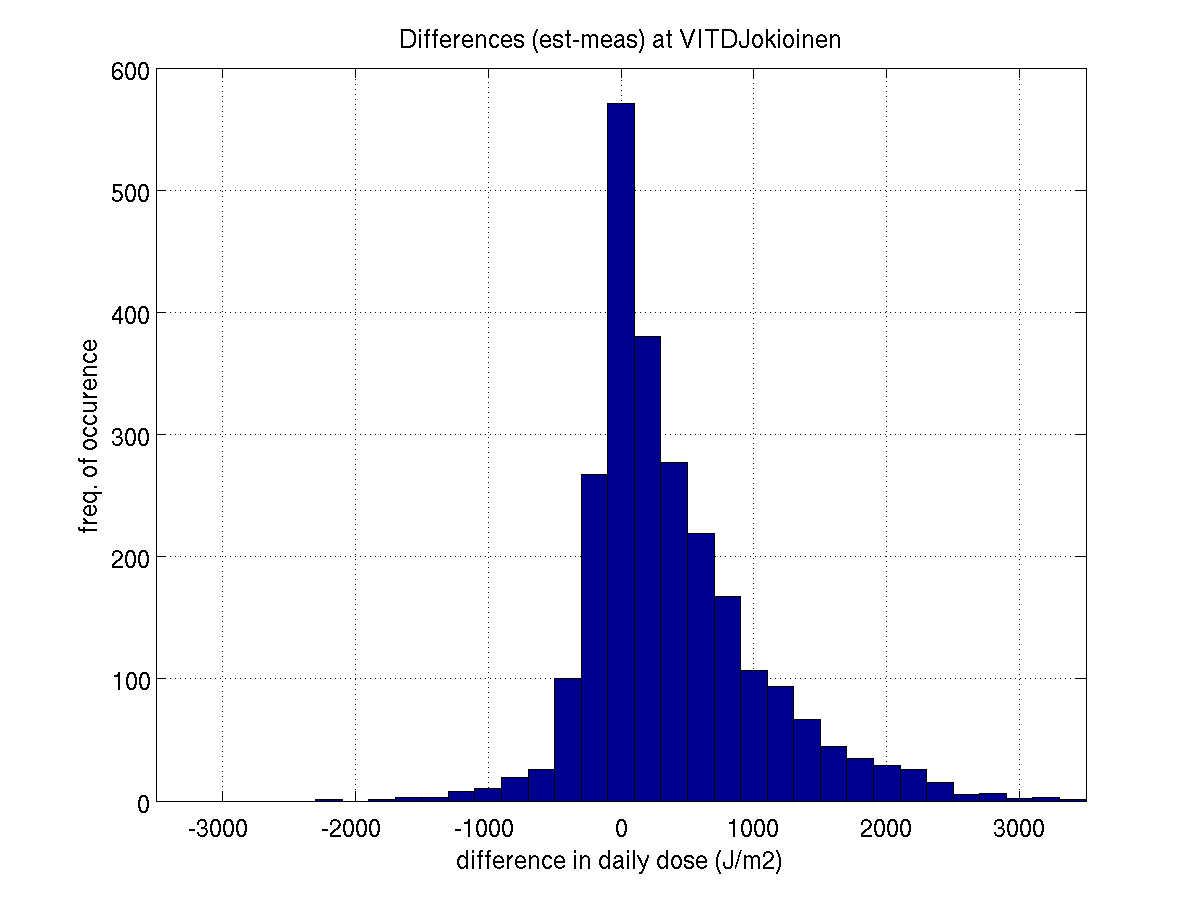
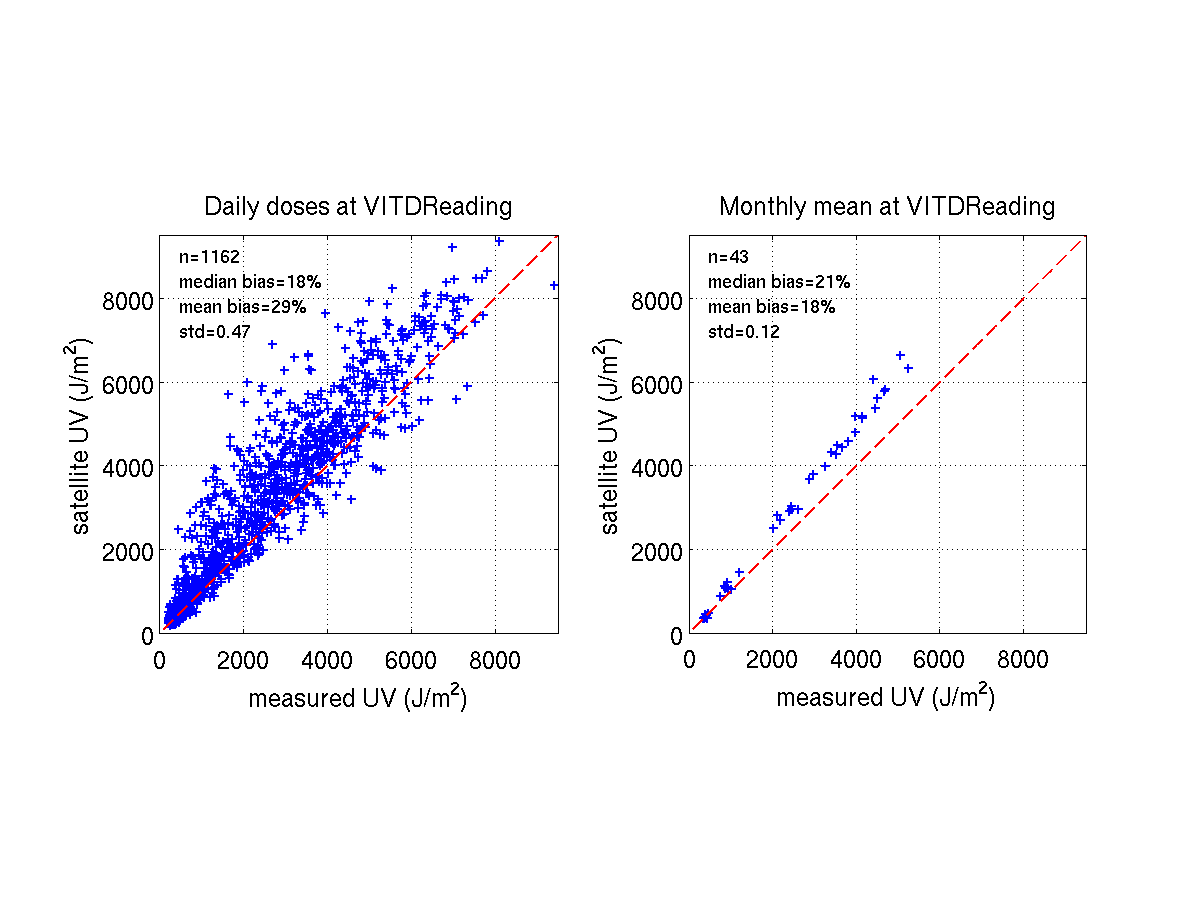
In addition to this summarizing table, we include some illustrative figures
of the validation results at each station. These figures show,
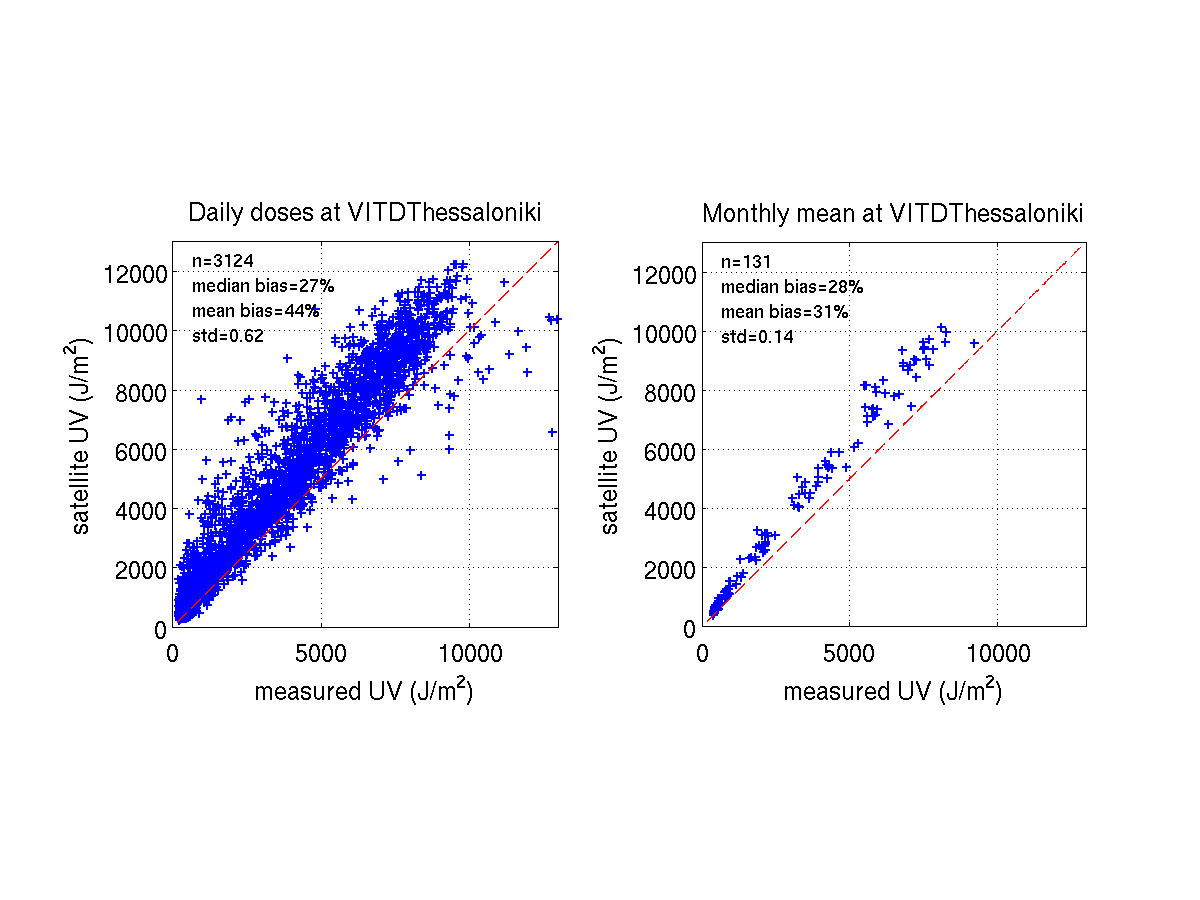
for instance, how some of the daily errors are averaged out when looking
at longer periods: the performance for the monthly mean values is clearly
better than for daily values, indicating that the method has potential to
serve as an information source for time series studies.
Look at the figures for the validation of satellite daily data data against ground based instruments:
Satellite data against ground-based instruments:
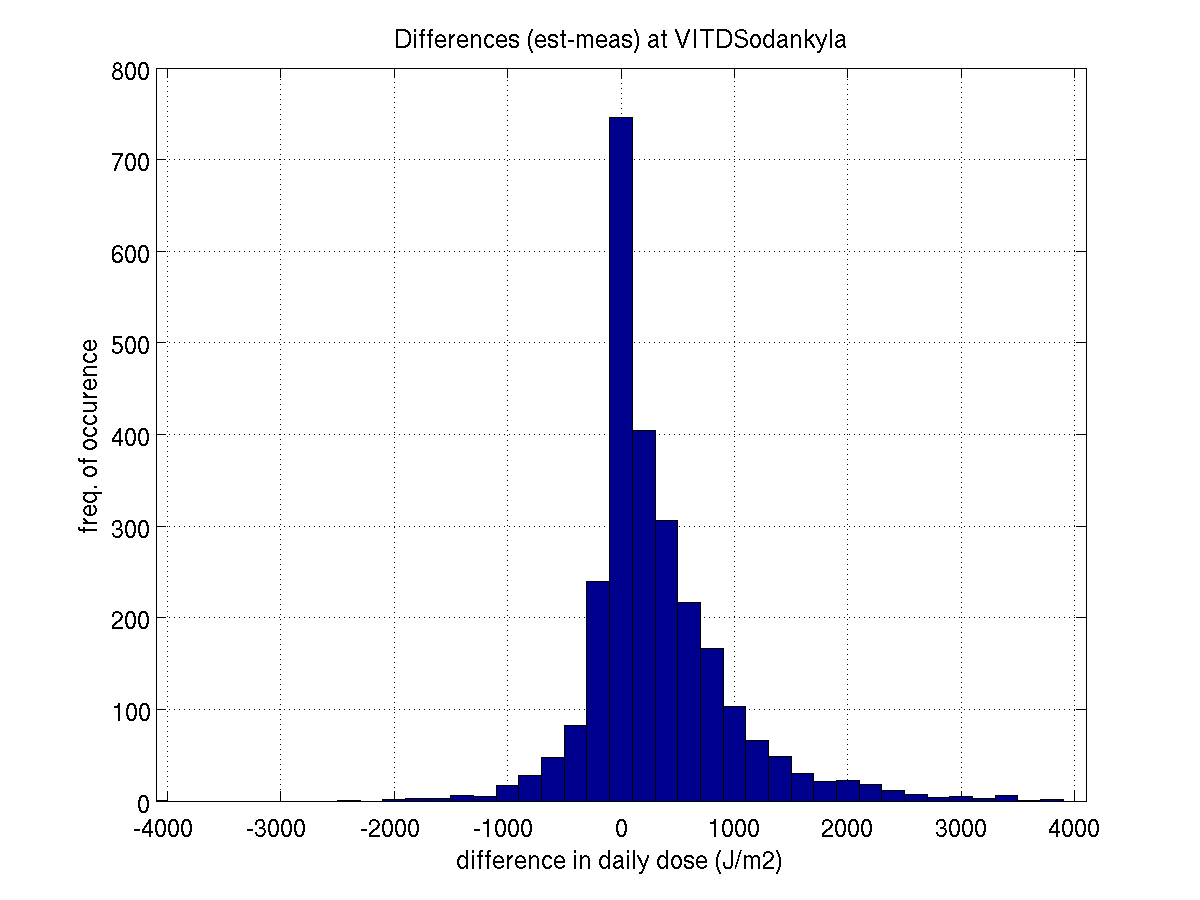
SODANKYLA
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
JOKIOINEN
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
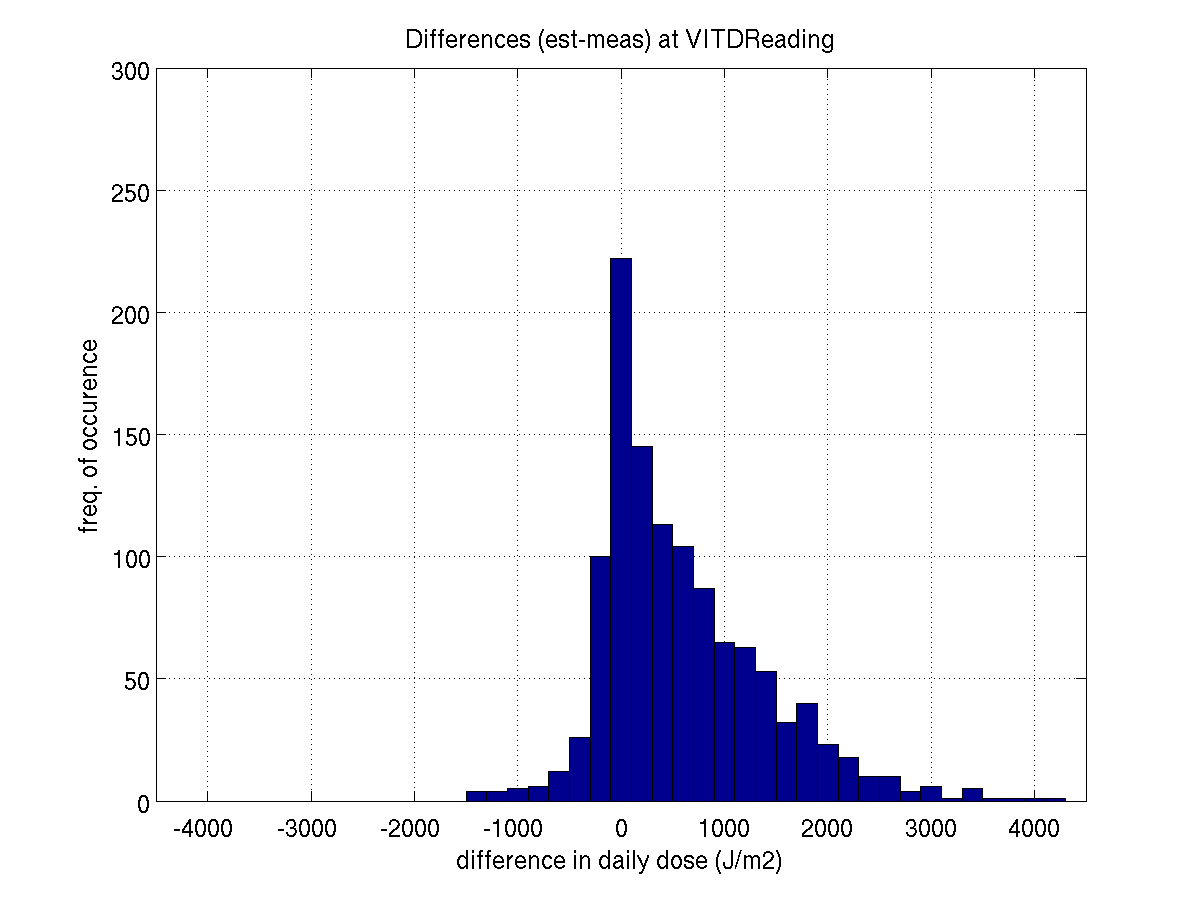
READING
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
THESSALONIKI
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
 Back to the list
Back to the list,
To the top of page
Jussi Kaurola, 31 August 2009